Copaifera multijuga Hayne - Fabaceae - syn..Copaiba multijuga (Hayne) Kuntze - Brazilian copaiba, Copaiva
Large evergreen tree, native to Brazil (Amazonas, Bahia, Pará) and Bolivia (Pando). tropicos.org
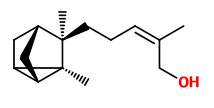
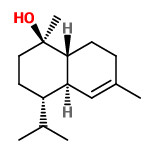
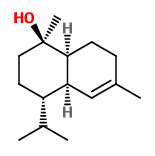
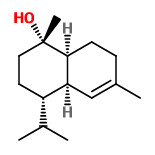
„Copaifera multijuga Hayne is one of the Copaifera species from which copaiba oil is extracted. Employed in the composition of anti-inflammatory and antiseptic products used in phytotherapy, it is also used by the fragrance industry as a fixative in perfumes, cosmetics and in products such as soaps. To identify the active aroma compounds in C. multijuga oil bouquet, GC-O-MS using AEDA (Aroma Extract Dilution Analysis) was used after the quantification of the components by GC-FID. The results obtained pointed to minor compounds such as δ-cadinene (1.9%, FD 64), δ-cadinol (0.9%, FD 128), (Z)-α-santalol (0.2%, FD 128), caryophyllene oxide (0.2%, FD 64), α-cadinol (0.1%, FD 128) and τ-muurolol (0.1%, FD 128) as the most intense compounds in the odor of the copaiba oil studied. Chiral GC-O-MS showed (+)-δ-cadinene as the only enantiomer present in the oil, with a sweet, green and refreshing aroma.“
Major volatile components of the hexane extract from copaiba oleoresin were (E)-β-caryophyllene (60.2%, spicy-woody, FD 2), α-humulene (8.6%, floral-woody, FD 2), α-bergamotene (6.4%, floral-woody, FD 2), and α-copaene (4.2%, woody, FD 2).
Sant'Anna, Beatriz MP, et al. "Characterization of woody odorant contributors in copaiba oil (Copaifera multijuga Hayne)." Journal of the Brazilian Chemical Society 18.5 (2007): 984-989

Copaifera multijuga, Iranduba, Brazil (2024) © mapoflife_rapidassessments CC BY-SA 4.0 inaturalist.org